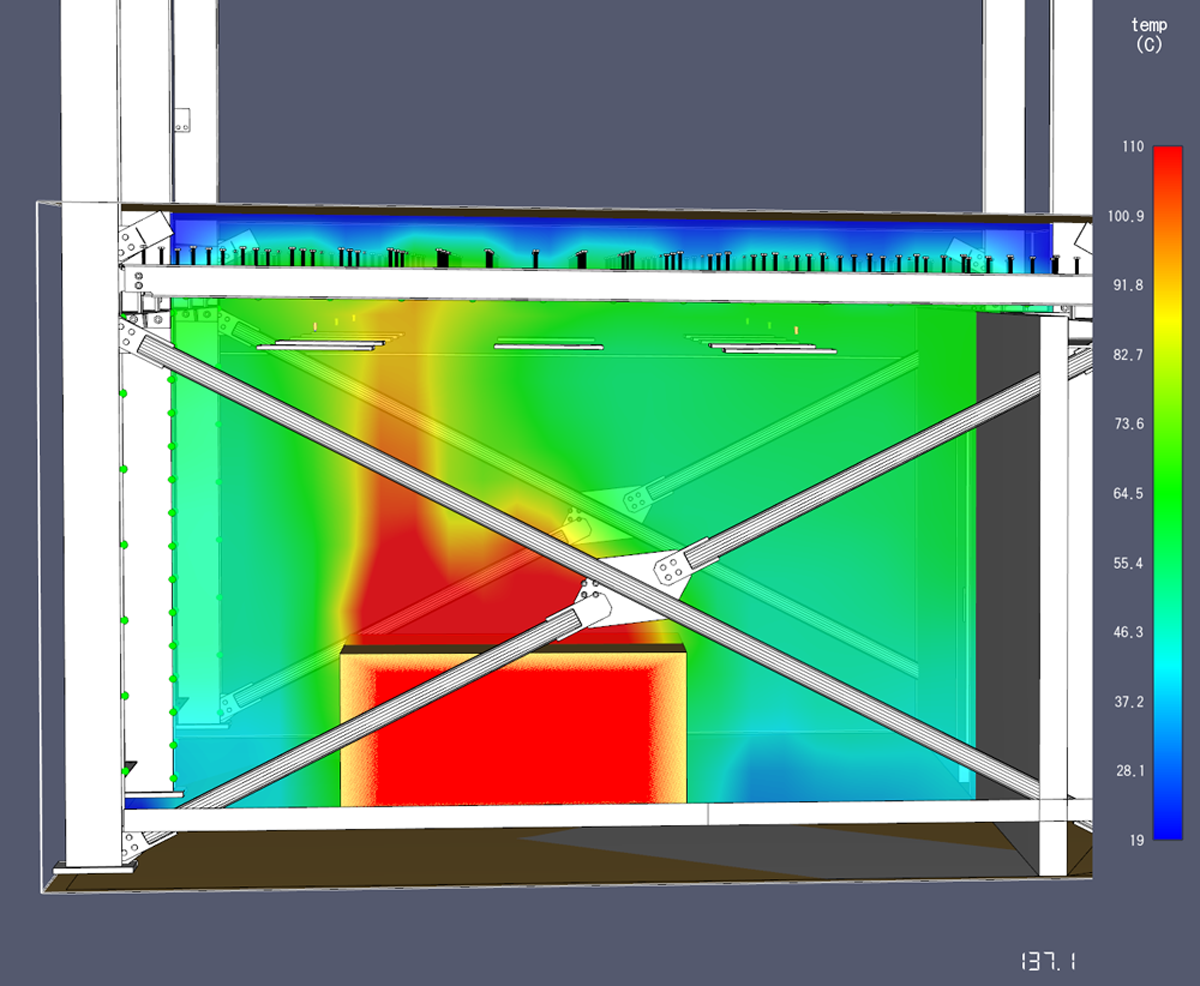
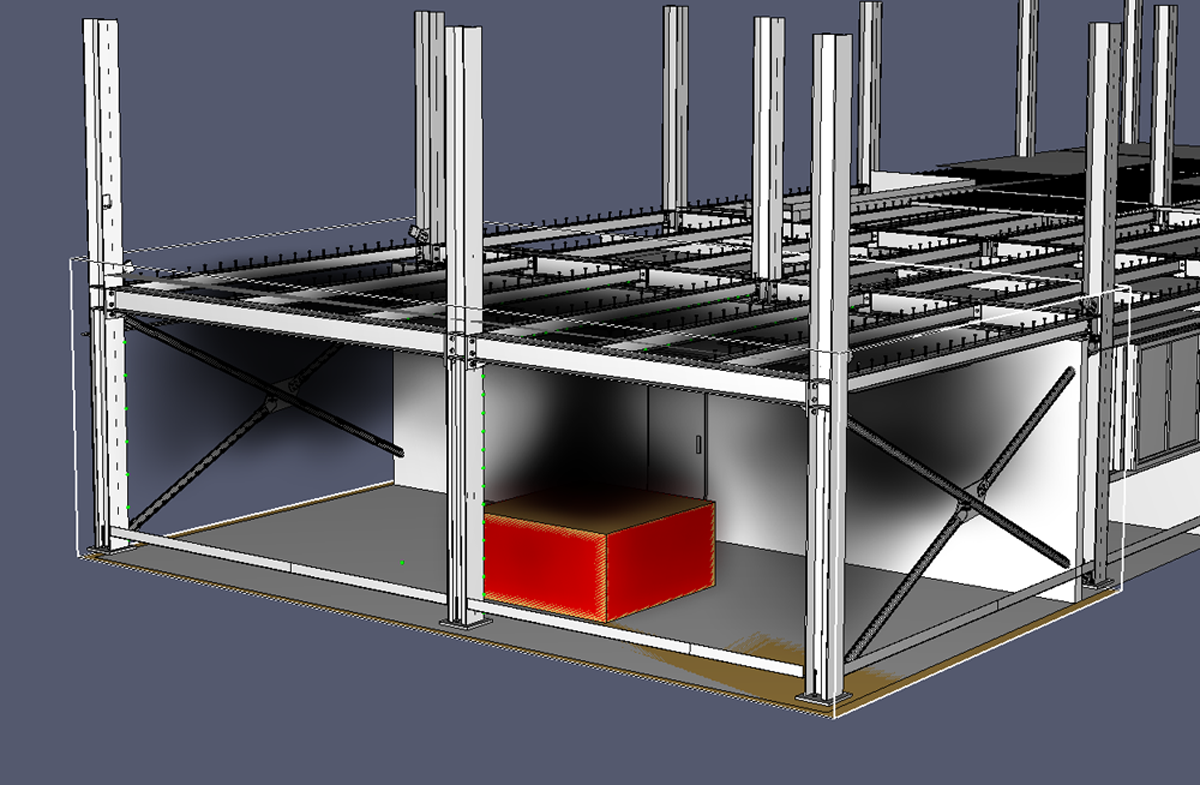
CFD modeliranje
CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) modeliranje dio je mehanike fluida koji uz pomoć numeričkih metoda i algoritama rješava i analizira probleme koji se odnose na tokove kretanja fluida. Za izračunavanje složenih
numeričkih izraza koriste se verificirani računalni programi.
Numeričke metode na kojima se bazira izračun su: metoda konačnih volumena (MKV) i Navier-Stokesove jednadžbe. Navier-Stokesove jednadžbe nazvane su po Claude-Luis Navieru i George Gabriel Stokesu, a predstavljaju sustav jednadžbi koji opisuje gibanje čestica fluida kao što su tekućine i plinovi. Te jednadžbe temelje se na pretpostavci da su promjene u momentu (akceleraciji) čestica fluida rezultati promjena u tlaku i disipativnim viskoznim silama (unutrašnje trenje fluida) koje se odvijaju unutar fluida.
Navier-Stokesove jednadžbe odnose se na strujanje newtonskog, jedno-komponentnog jednofaznog fluida (dakle bez kemijske reakcije) i bez utjecaja elektro-magnetskih sila.
Metoda konačnih volumena (MKV) metoda je za numeričko rješavanje diferencijalnih jednadžbi. U usporedbi sa standardnim aparatom za diskretizaciju, tj. s metodom konačnih elemenata (MKE) i metodom konačnih diferencija (MKD), za MKV se često kaže da zauzima mjesto između, jer se ponekad smatra generalizacijom MKD, a ponekad specijalnim slučajem MKE. MKV se javlja 1960-ih godina za potrebe računanja kod zadaća povezanih s nuklearnim reaktorima i difuzijama neutrona. 1970-ih se razvija i za potrebe mehanike fluida. Ali tek je u posljednja tri desetljeća postala vrlo popularna te se danas najviše koristi u aerodinamici, mehanici fluida, fizici čvrstog stanja, izradi CFD modela i dr. Povećanjem procesorske snage osobnih računala CFD modeliranje požara zadnjih godina postaje vrlo važan alat u požarnom inženjerstvu.
CFD modeli koje koristimo prilikom projektiranja mogu predvidjeti temperaturu, količine dima, koncentraciju ugljičnog monoksida i drugih produkata izgaranja sve u realnom vremenu tijekom požara. Rezultati požarnih simulacija koriste se za utvrđivanje sigurnosti građevine u fazi projektiranja prije same izgradnje, procjenu sigurnosti već postojećih građevina, u svrhu rekonstrukcije događaja u sklopu istrage nakon realnog požara te kao pomoć pri obuci vatrogasaca.
CFD modeling
CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) modeling is a part of fluid mechanics that, with the help of numerical methods and algorithms, solves and analyzes problems related to fluid flow. Verified computer programs are used to calculate complex numerical expressions.
The numerical methods on which the calculation is based are: the finite volume method (FVM) and the Navier-Stokes equation. The Navier-Stokes equations are named after Claude-Luis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, and represent a system of equations that describes the motion of fluid particles such as liquids and gases. These equations are based on the assumption that changes in the moment (acceleration) of fluid particles are the result of changes in pressure and dissipative viscous forces (internal fluid friction) that take place inside the fluid.
Navier-Stokes equations refer to the flow of a Newtonian, single-component, single-phase fluid (therefore without chemical reaction) and without the influence of electro-magnetic forces.
The finite volume method (FVM) is a method for numerically solving differential equations. Compared to the standard discretization apparatus, i.e. Finite Element Method (FEM) and Finite Difference Method (FDM), FDM is often said to occupy an in-between place, as it is sometimes considered a generalization of FEM and sometimes a special case of FEM. MKV appeared in the 1960s for computational purposes in tasks related to nuclear reactors and neutron diffusion. In the 1970s, it was also developed for the needs of fluid mechanics. But it only became very popular in the last three decades and today it is mostly used in aerodynamics, fluid mechanics, solid state physics, CFD model creation, etc. With the increase in the processing power of personal computers, CFD fire modeling has become a very important tool in fire engineering in recent years.
The CFD models we use during design can predict temperature, smoke amounts, concentration of carbon monoxide and other combustion products all in real time during a fire. The results of fire simulations are used to determine the safety of the building in the design phase before construction itself, to assess the safety of already existing buildings, for the purpose of reconstructing events as part of the investigation after a real fire, and as an aid in the training of firefighters.
CFD-Modellierung
Die CFD-Modellierung (Computational Fluid Dynamics) ist ein Teilbereich der Strömungsmechanik, der mit Hilfe numerischer Methoden und Algorithmen Probleme im Zusammenhang mit Strömungen löst und analysiert. Zur Berechnung komplexer numerischer Ausdrücke werden verifizierte Computerprogramme verwendet. Die der Berechnung zugrunde liegenden numerischen Methoden sind: die Finite-Volumen-Methode (FVM) und die Navier-Stokes-Gleichung. Die Navier-Stokes-Gleichungen sind nach Claude-Luis Navier und George Gabriel Stokes benannt und stellen ein Gleichungssystem dar, das die Bewegung von Fluidteilchen wie Flüssigkeiten und Gasen beschreibt. Diese Gleichungen basieren auf der Annahme, dass Änderungen des Moments (Beschleunigung) von Fluidteilchen das Ergebnis von Druckänderungen und dissipativen viskosen Kräften (innere Flüssigkeitsreibung) sind, die innerhalb des Fluids stattfinden. Navier-Stokes-Gleichungen beziehen sich auf die Strömung eines Newtonschen, einkomponentigen, einphasigen Fluids (also ohne chemische Reaktion) und ohne den Einfluss elektromagnetischer Kräfte. Die Finite-Volumen-Methode (FVM) ist ein Verfahren zum numerischen Lösen von Differentialgleichungen. Im Vergleich zu den Standard-Diskretisierungsapparaten, also der Finite-Elemente-Methode (FEM) und der Finite-Differenzen-Methode (FDM), wird der FDM oft eine Zwischenstellung nachgesagt, da sie manchmal als Verallgemeinerung der FDM und manchmal als Sonderfall der FEM angesehen wird . MKV erschien in den 1960er Jahren für Rechenzwecke bei Aufgaben im Zusammenhang mit Kernreaktoren und Neutronendiffusion. In den 1970er Jahren wurde es auch für die Bedürfnisse der Strömungsmechanik entwickelt. Aber erst in den letzten drei Jahrzehnten wurde es sehr populär und wird heute hauptsächlich in der Aerodynamik, Strömungsmechanik, Festkörperphysik, Erstellung von CFD-Modellen usw. verwendet. Mit der Steigerung der Rechenleistung von PCs ist die CFD-Brandmodellierung in den letzten Jahren zu einem sehr wichtigen Werkzeug in der Brandschutztechnik geworden. Die CFD-Modelle, die wir während der Konstruktion verwenden, können Temperatur, Rauchmengen, Konzentration von Kohlenmonoxid und andere Verbrennungsprodukte während eines Feuers in Echtzeit vorhersagen. Die Ergebnisse von Brandsimulationen werden zur Ermittlung der Gebäudesicherheit in der Planungsphase vor dem eigentlichen Bau, zur Bewertung der Sicherheit bereits bestehender Gebäude, zur Rekonstruktion von Ereignissen im Rahmen der Untersuchung nach einem realen Brand sowie als Unterstützung bei der Ausbildung von Feuerwehrleuten.
Elaborat zaštite od požara
Elaborat zaštite od požara predstavlja temeljni dokument kojim se definiraju tehnička rješenja iz područja zaštite od požara. Sukladno važećim zakonskim odredbama on predstavlja podlogu za izradu glavnog projekta i pritom mjere predviđene Elaboratom utječu na sve dijelove projektne dokumentacije. Elaboratom je potrebno realno i cjelovito sagledati sve potencijalne opasnosti od požara na predmetnoj građevini te primjenom važeće zakonske regulative, priznatih pravila tehničke prakse kao i računalnih modela i proračuna, pružiti projektantima optimalan koncept zaštite od požara građevine. Skupa tehnička rješenja koja mogu proizaći iz Elaborata zaštite od požara ne znače ujedno da će u građevini biti postignut i zadovoljavajući nivo sigurnosti. Čest je slučaj da se prilikom izrade Elaborata pretjeruje s određenim tehničkim rješenjima ne sagledavajući pri tome stvarnu snagu požara koji se može razviti u građevini kao ni njegovu termodinamiku širenja. Ovo za posljedicu može imati da se neke predviđene mjere zaštite od požara mogu u realnim uvjetima pokazati kao u potpunosti nepotrebne.
Elaborate on fire protection
Elaborate on the fire protection report is a basic document that defines technical solutions in the field of fire protection.
In accordance with the applicable legal provisions, it represents the basis for the creation of the main project, and at the same time, the measures provided for in the Elaborate affect all parts of the project documentation. With the elaboration, it is necessary to realistically and comprehensively look at all potential fire hazards in the building in question, and by applying the current legal regulations, recognized rules of technical practice as well as computer models and calculations, provide designers with an optimal concept of fire protection of the building. Expensive technical solutions that can result from the Fire Protection Elaboration do not mean that a satisfactory level of safety will be achieved in the building. It is often the case that when preparing the Elaboration, certain technical solutions are exaggerated without taking into account the real strength of the fire that can develop in the building, as well as the thermodynamics of its spread. This may result in some anticipated fire protection measures being completely unnecessary in real conditions.
Brandschutzdokument
Das Brandschutzdokument ist ein Grundlagendokument, das technische Lösungen im Bereich des Brandschutzes definiert. Gemäß den geltenden gesetzlichen Bestimmungen stellt es die Grundlage für die Erstellung des Hauptprojekts dar, gleichzeitig wirken sich die im Dokument vorgesehenen Maßnahmen auf alle Teile der Projektdokumentation aus. Im Dokument ist es notwendig, alle potenziellen Brandgefahren im jeweiligen Gebäude realistisch und umfassend zu betrachten und unter Anwendung der aktuellen gesetzlichen Vorschriften, anerkannten Regeln der Technik sowie Computermodelle und Berechnungen Planern ein optimales Konzept zu liefern des Brandschutzes des Gebäudes. Teure technische Lösungen, die sich aus dem Dokument ergeben können, führen nicht dazu, dass ein zufriedenstellendes Sicherheitsniveau im Gebäude erreicht wird. Es kommt häufig vor, dass bei der Erstellung des Dokuments bestimmte technische Lösungen übertrieben werden, ohne die tatsächliche Stärke des Brandes, der sich im Gebäude entwickeln kann, sowie die Thermodynamik seiner Ausbreitung zu berücksichtigen. Dies kann dazu führen, dass einige zu erwartende Brandschutzmaßnahmen unter realen Bedingungen völlig unnötig sind.
Procjena ugroženosti od požara i tehnološke eksplozije
Procjena ugroženosti od požara i tehnološke eksplozije predstavlja kompleksan dokument kojim se analizira i u konačnici ocjenjuje sigurnost postojećih građevina s aspekta zaštite od požara. Sukladno odredbama Zakona o zaštiti od požara (N.N. br. 92/10.) Procjenu su dužne izraditi sve pravne osobe, koje su prema rješenju Ministarstva unutarnjih poslova RH razvrstane u I. i II. kategoriju ugroženosti objekata od požara u skladu s Pravilnikom o razvrstavanju građevina, građevinskih dijelova i prostora u kategorije ugroženosti od požara (N.N. br. 62/94. i 32/97.). Sadržaj Procjene definiran je Pravilnikom o izradi procjene ugroženosti od požara i tehnološke eksplozije (N.N. br. 35/94.). Procjenu izrađuje tim od četiri stručnjaka različitih profila. Izradom Procjene rukovodi voditelj tima koji mora imati minimalno pet godina radnog iskustva na poslovima zaštite od požara.
Fire and technological explosion risk assessment
The fire and technological explosion risk assessment is a complex document that analyzes and ultimately evaluates the safety of existing buildings from the aspect of fire protection. In accordance with the provisions of the Law on Fire Protection (N.N. No. 92/10), the assessment is required to be made by all legal entities, which according to the decision of the Ministry of the Interior of the Republic of Croatia are classified into I. and II. fire hazard category of buildings in accordance with the Ordinance on classification of buildings, construction parts and spaces into fire hazard categories (N.N. no. 62/94 and 32/97). The content of the Assessment is defined by the Ordinance on the preparation of fire and technological explosion hazard assessment (N.N. No. 35/94.). The assessment is made by a team of four experts with different profiles. The creation of the Assessment is managed by the team leader who must have a minimum of five years of work experience in fire protection.
Bewertung des Brand- und technologischen Explosionsrisikos
Die Brand- und Explosionstechnische Gefährdungsbeurteilung ist ein komplexes Dokument, das die Sicherheit bestehender Gebäude unter brandschutztechnischen Gesichtspunkten analysiert und abschließend bewertet. Gemäß den Bestimmungen des Brandschutzgesetzes (N.N. Nr. 92/10) muss die Bewertung von allen juristischen Personen durchgeführt werden, die gemäß der Entscheidung des Innenministeriums der Republik Kroatien klassifiziert sind in I. und II. Brandgefahrenklasse von Gebäuden gemäß der Verordnung über die Einstufung von Gebäuden, Bauteilen und Räumen in Brandgefahrenklassen (N.N. Nr. 62/94 und 32/97). Der Inhalt der Bewertung wird durch die Verordnung über die Erstellung einer brand- und technologischen Explosionsgefährdungsbewertung (N.N. Nr. 35/94.) festgelegt. Die Bewertung erfolgt durch ein Team aus vier Experten mit unterschiedlichen Profilen. Die Erstellung des Assessments wird vom Teamleiter geleitet, der über mindestens fünf Jahre Berufserfahrung im Brandschutz verfügen muss.
Plan zaštite od požara
Plan zaštite od požara izrađuje se na temelju Procjene ugroženosti od požara i tehnoloških eksplozija, odnosno sve pravne osobe koje su dužne izrađivati Procjenu ugroženosti od požara moraju imati i Plan. Ovaj Plan sastoji se od tekstualnog i grafičkog dijela, a izrađuje se za pojedinačnu građevinu, postrojenje i prostor. Detaljni sadržaj definiran je Pravilnikom o planu zaštite od požara (N.N. br. 51/12.).
Fire protection plan
The fire protection plan is drawn up on the basis of the fire and technological explosion hazard assessment, that is, all legal entities that are obliged to draw up the fire hazard assessment must also have a plan. This Plan consists of a textual and graphic part, and is prepared for an individual building, plant and space. The detailed content is defined by the Ordinance on fire protection plan (N.N. no. 51/12.).
Brandschutzplan
Das Brandschutzkonzept wird auf der Grundlage der brand- und technologischen Explosionsgefährdungsbeurteilung erstellt, d. h. alle juristischen Personen, die zur Erstellung der Brandgefährdungsbeurteilung verpflichtet sind, müssen auch über ein Brandschutzkonzept verfügen. Dieser Plan besteht aus einem textuellen und einem grafischen Teil und wird für ein einzelnes Gebäude, eine Anlage und ein Gebiet erstellt. Der genaue Inhalt wird durch die Verordnung über den Brandschutzplan (N.N. Nr. 51/12.) festgelegt.
Opći akti iz zaštite od požara / General acts on fire protection / Allgemeine Brandschutzgesetze
Consulting usluge na području zaštite od požara / Consulting services in the field of fire protection / Beratungsdienstleistungen auf dem Gebiet des Brandschutzes
Osposobljavanje za provedbu preventivnih mjera zaštite od požara / Training for the implementation of preventive fire protection measures /Schulung zur Umsetzung vorbeugender Brandschutzmaßnahmen